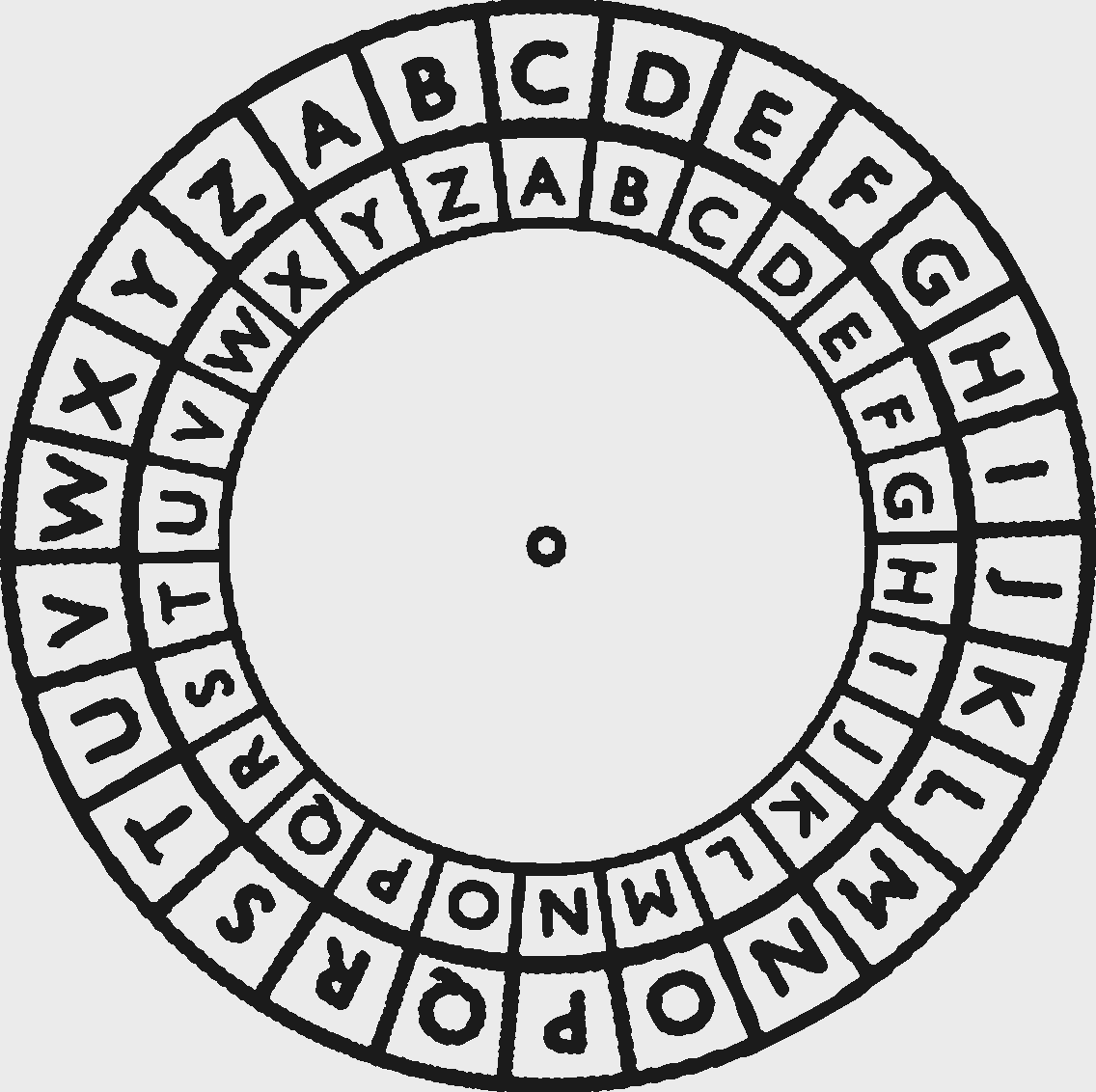
Tool for encrypting/decrypting with the disk cipher also called wheel (or dial), a visual tool facilitating mono-alphabetic substitution.
Cipher Disk/Wheel - dCode
Tag(s) : Substitution Cipher
dCode is free and its tools are a valuable help in games, maths, geocaching, puzzles and problems to solve every day!
A suggestion ? a feedback ? a bug ? an idea ? Write to dCode!
Cipher Disk/Wheel
Disk Cipher Decoder
Disk Cipher Encoder
Answers to Questions (FAQ)
What is a disk cipher? (Definition)
A cipher disc is a mechanical tool made up of 2 dials (1 inner disc and 1 outer disc) making it possible to represent a mono-alphabetic substitution by rotating the discs relative to each other. The alignment of the boxes thus obtained indicates the correspondence of the letters. Here is an example of an (empty) disk that can be filled with the 26 letters of the alphabet 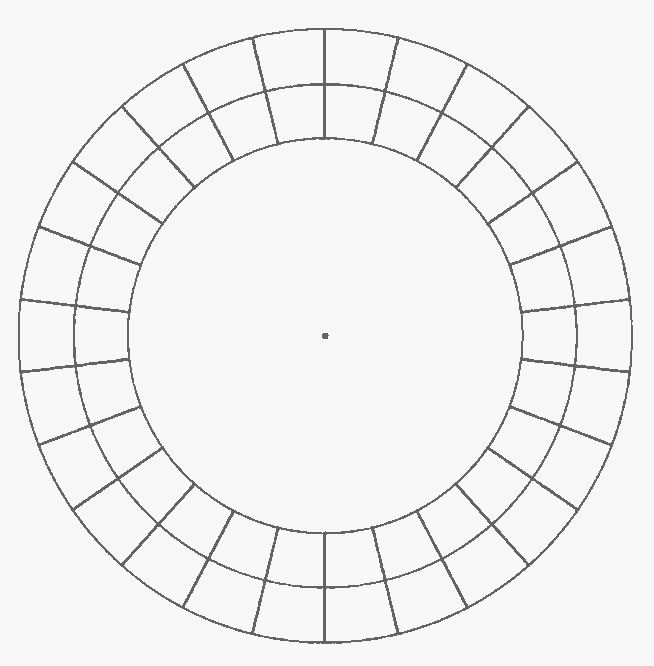
Generally, at least 1 of the 2 discs contains the alphabet in its classic order: ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ, the second can be different and contain a disordered alphabet.
Often, the inner disk is used as a reference for the plain letters, and the outer disk is used for the coded letters.
How to encrypt using a disk cipher?
Select a position for the disc (by rotating the inner or outer dial) and the reference disc for the plain message letters.
For each letter of the message to be encrypted, locate the letter on the plain disc and note the corresponding letter located opposite on the encrypted disc.
How to decrypt a disk cipher?
Position the disc at a defined offset.
For each letter of the coded message, locate the letter on the encrypted disc and note the corresponding letter opposite on the plain disc.
How to set disk position?
Choosing the position of the disc means indicating which letters correspond to which others. There are several methods:
— Give a 2-letter key, defining a couple (plain letter-encrypted letter), the user must then align the 2 letters before starting an encryption (or decryption). Sometimes the letters are next to each other: AB or separated by a hyphen A-B or by the equal sign A=B.
— Give only one letter, the second letter omitted being the plain letter A.
— Give a number, defining the offset value of the rotating disk (usually exterior) with respect to the fixed disk (usually interior), a positive value indicating the clockwise direction and a negative value indicating the counterclockwise direction.
How to recognize a disk ciphertext? (Identification)
A disk encryption is nothing more than an alphabetical substitution. Using disk makes it easier to encrypt/decrypt by hand.
The index of coincidence of a disk-encrypted message is therefore similar to that of the plain message.
The frequency analysis should highlight the coding letter for E.
The notions of disc, wheel or dial are clues.
What are the variants of the disk cipher?
The disk cipher allows to represent any substitution like the Caesar cipher, or the Atbash code.
Alberti proposed the use of cipher disks and improved its security slightly by proposing to periodically shift/rotate the disk according to a defined period and increment, see Alberti's cipher.
Source code
dCode retains ownership of the "Cipher Disk/Wheel" source code. Any algorithm for the "Cipher Disk/Wheel" algorithm, applet or snippet or script (converter, solver, encryption / decryption, encoding / decoding, ciphering / deciphering, breaker, translator), or any "Cipher Disk/Wheel" functions (calculate, convert, solve, decrypt / encrypt, decipher / cipher, decode / encode, translate) written in any informatic language (Python, Java, PHP, C#, Javascript, Matlab, etc.) or any database download or API access for "Cipher Disk/Wheel" or any other element are not public (except explicit open source licence). Same with the download for offline use on PC, mobile, tablet, iPhone or Android app.
Reminder: dCode is an educational and teaching resource, accessible online for free and for everyone.
Cite dCode
The content of the page "Cipher Disk/Wheel" and its results may be freely copied and reused, including for commercial purposes, provided that dCode.fr is cited as the source (Creative Commons CC-BY free distribution license).
Exporting the results is free and can be done simply by clicking on the export icons ⤓ (.csv or .txt format) or ⧉ (copy and paste).
To cite dCode.fr on another website, use the link:
In a scientific article or book, the recommended bibliographic citation is: Cipher Disk/Wheel on dCode.fr [online website], retrieved on 2026-01-22,