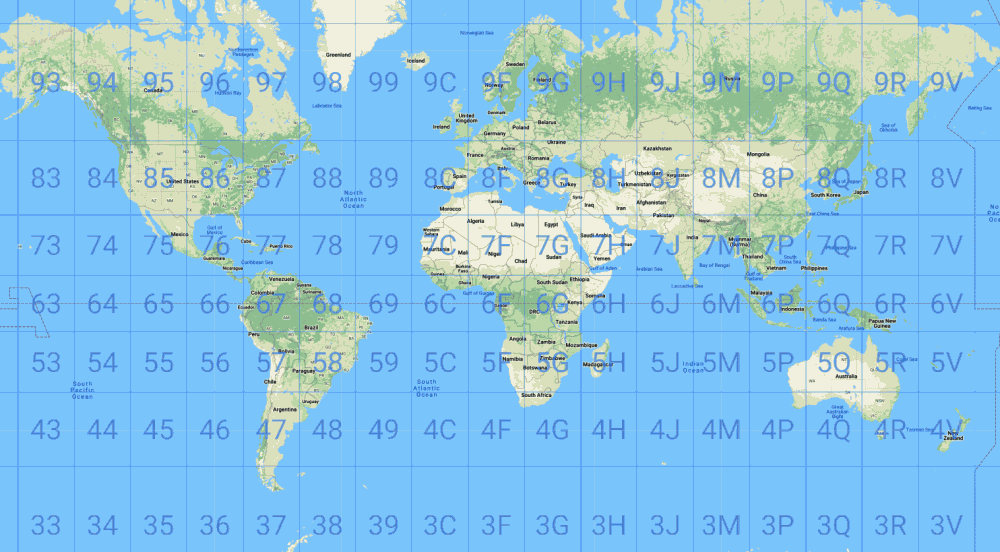
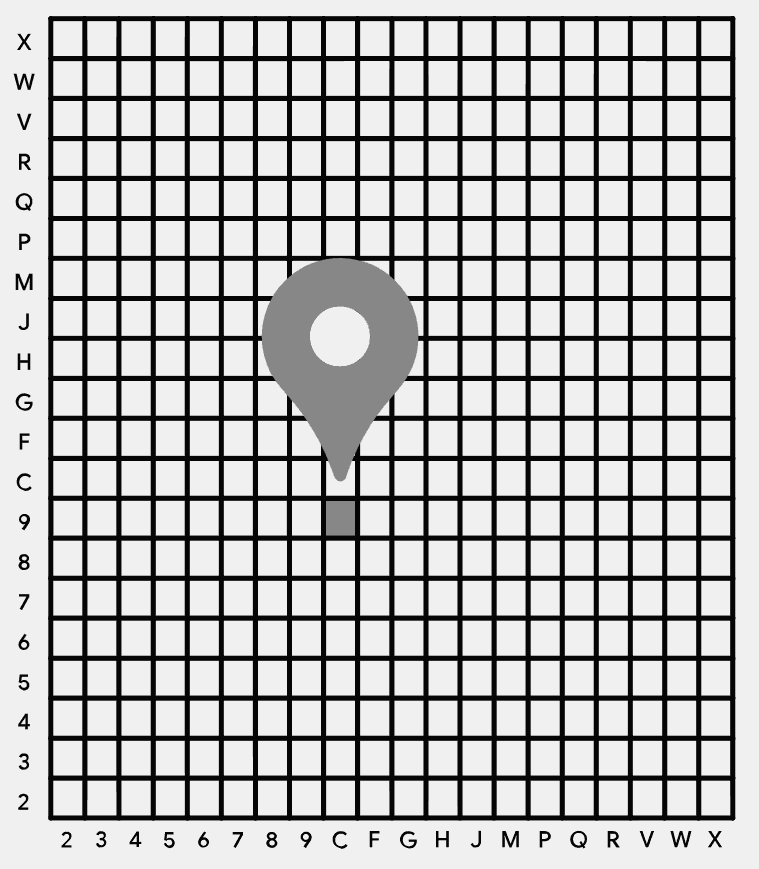
Tool to convert open location codes to GPS coordinates on a map. Open Location is a geocoding system created by Google (sometimes renamed 'plus codes') and displayed, among others, on Google Maps.
Open Location (Plus Code) - dCode
Tag(s) : Geography
dCode is free and its tools are a valuable help in games, maths, geocaching, puzzles and problems to solve every day!
A suggestion ? a feedback ? a bug ? an idea ? Write to dCode!
Open Location (Plus Code)
Open Location Converter
Answers to Questions (FAQ)
What is an Open Location code OLC? (Definition)
Open Location Codes (OLC), also known as Plus Codes, are an open-source system developed by Google to represent any geographic location on Earth using a short, easy-to-communicate alphanumeric code. Unlike traditional GPS coordinates, a Plus Code is shorter and more readable.
How do Open Location codes work?
The Earth is first divided into a grid of 18 columns by 9 rows, each cell covering 20° of longitude and 20° of latitude. Each area is then subdivided into a 20x20 grid, and this process can be repeated up to five times to refine the accuracy.
The final optional level further divides the area into a 4x5 grid, providing a maximum accuracy of approximately 3.5 meters.
A code is made up of 2 parts separated by a plus sign + of the form AABBCCDD+EEF or AABB+CC. The first part is made up of 1 to 4 alphanumeric pairs (BB,CC,DD are optional), the second part is also optional, but the fewer letters there are, the less precise the location.
The plus sign is also optional, but it is part of the signature of the code and makes it easier to read.
The 20 characters authorized to code the zones are 23456789CFGHJMPQRVWX (they are used as base 20 writing)
How to convert an Open Location code into GPS?
Separate the pairs of characters and for each, note the first character (latitude coordinate) and the second character (longitude coordinate) to locate in the grid.
To reconstruct GPS coordinates (latitude, longitude), it is first necessary to convert the characters 23456789CFGHJMPQRVWX according to the correspondence table:
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | C | F | G | H | J | M | P | Q | R | V | W | X |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
Then for each value, multiply it by the precision of each couple according to the table
| #1 AA | 20° |
| #2 BB | 1° |
| #3 CC | 0.05° |
| #4 DD | 0.0025° |
| #5 EE | 0.000125° |
| #6 F | 0.00003125° |
Add all latitude values and subtract 90° on one side and all longitude values and subtract 180° on the other to obtain GPS coordinates.
Example: The code 8FW4V75R+8W is cut into pairs 8F,W4,V7,5R,8W
The first pair 8F consists of latitude $ \texttt{8} \rightarrow 6 \times 20° = 120° $ and longitude $ \texttt{F} \rightarrow 9 \times 20° = 180° $
The second pair is' W4' either latitude +18° and longitude +2° etc.
The sums respect give the latitude $ \approx 138.8583 - 90 = 48.8583° $ and the longitude $ \approx 182.2923 - 180 = 2.2923° $ so the GPS coordinates $ (48.8583, 2.2923) $
How to convert GPS coordinates to Open Location codes?
From GPS coordinates:
Example: (lat, long) = 48.8583,2.2923
1- add 90° to the latitude and 180° to the longitude
Example: $ 48.8583+90=138.8583 $, $ 2.2923+180=182.2923 $
2- multiply the values by 8000 (= 20 ^ 3)
Example: $ 138.8583 \times 8000 = 1110866.4 $, $ 182.2923 \times 8000 = 1458338.4 $
3- convert the values obtained to base 20 (with the alphabet 23456789CFGHJMPQRVWX) by limiting yourself to the whole part and supplementing with initial zeros if the result has less than 5 digits.
Example: $ 1110866_{(10)} = [6, 18, 17, 3, 6]_{(20)} = \texttt{8WV58} $, $ 1458338_{(10)} = [9, 2, 5, 16, 18]_{(20)} = \texttt{F47RW} $
4- insert the $ 2 \times 5 $ characters obtained by alternating latitude then longitude and write the result in the form 'XXXXXXXX + XX'
Example: 8WV58 and F47RW give 8F,W4,V7,5R,8W or the plus code 8FW4V75R+8W
How to recognize Open Location codes?
The Open Location (OLC) codes are in the format XXXXXXXX+XX or sometimes XXXX+XX Place (the first 4 characters are deleted - named short code) this second form requires a database in order to know the place which allows to find the 4 first characters.
Codes have a + hence their nickname plus codes
The Google company created these codes which are used more and more, thanks to Google Maps/Earth, any reference to the search engine is a clue.
References to travel, travelers, tourism, Earth, world, etc. are clues.
Where to insert the + sign?
The + sign is always placed after the eighth character of a complete code.
It is used to improve the readability of the code, but has no numerical value in the calculation.
How to convert plus code into address?
Source code
dCode retains ownership of the "Open Location (Plus Code)" source code. Any algorithm for the "Open Location (Plus Code)" algorithm, applet or snippet or script (converter, solver, encryption / decryption, encoding / decoding, ciphering / deciphering, breaker, translator), or any "Open Location (Plus Code)" functions (calculate, convert, solve, decrypt / encrypt, decipher / cipher, decode / encode, translate) written in any informatic language (Python, Java, PHP, C#, Javascript, Matlab, etc.) or any database download or API access for "Open Location (Plus Code)" or any other element are not public (except explicit open source licence). Same with the download for offline use on PC, mobile, tablet, iPhone or Android app.
Reminder: dCode is an educational and teaching resource, accessible online for free and for everyone.
Cite dCode
The content of the page "Open Location (Plus Code)" and its results may be freely copied and reused, including for commercial purposes, provided that dCode.fr is cited as the source (Creative Commons CC-BY free distribution license).
Exporting the results is free and can be done simply by clicking on the export icons ⤓ (.csv or .txt format) or ⧉ (copy and paste).
To cite dCode.fr on another website, use the link:
In a scientific article or book, the recommended bibliographic citation is: Open Location (Plus Code) on dCode.fr [online website], retrieved on 2026-01-20,
- Open Location Converter
- What is an Open Location code OLC? (Definition)
- How do Open Location codes work?
- How to convert an Open Location code into GPS?
- How to convert GPS coordinates to Open Location codes?
- How to recognize Open Location codes?
- Where to insert the + sign?
- How to convert plus code into address?